Pleural Effusions
Expert Diagnosis & Personalized Treatment for Fluid Around the Lungs
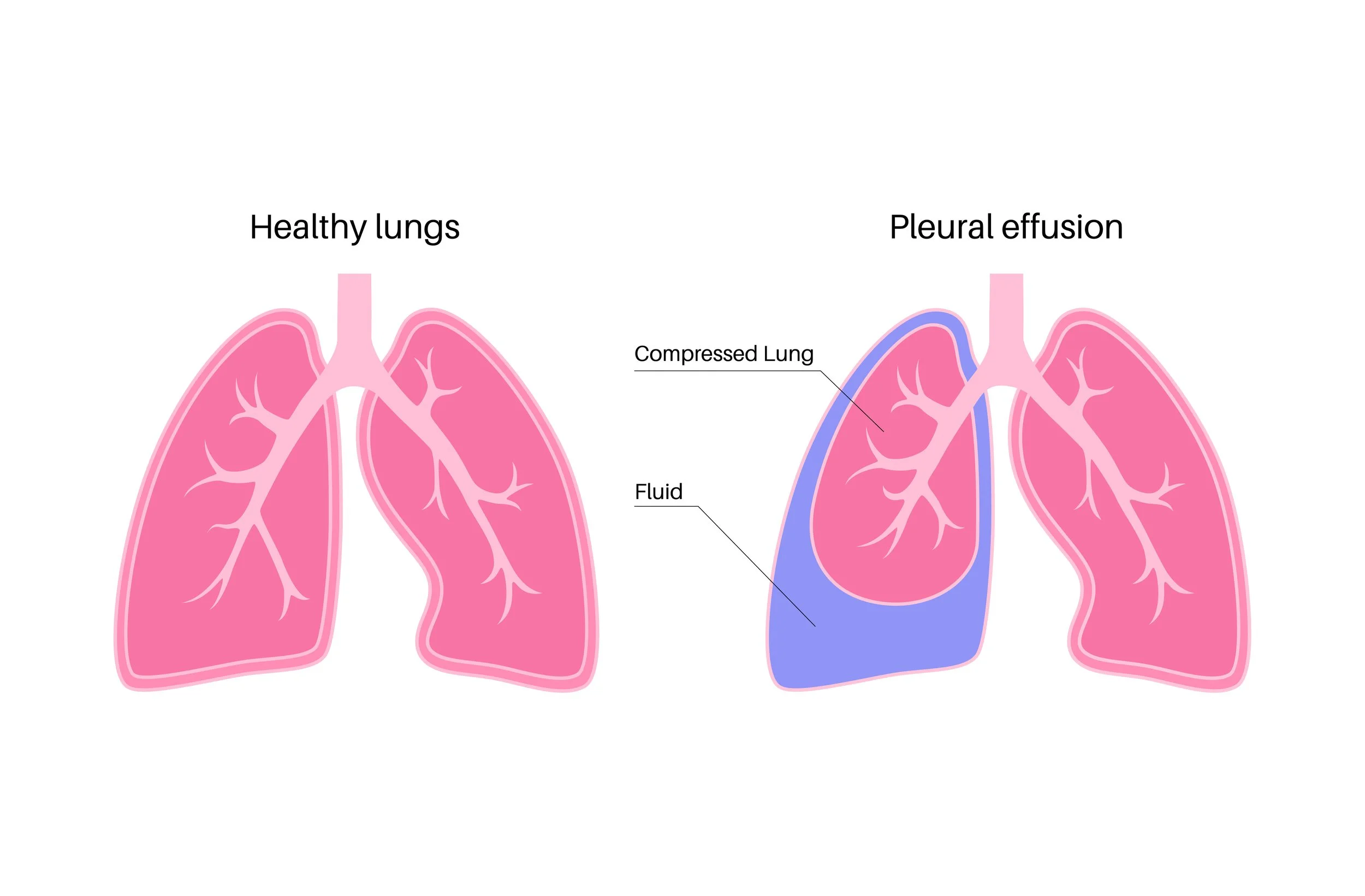
A pleural effusion occurs when excess fluid builds up in the space between the lungs and the chest wall, making it harder to breathe and causing discomfort. At The Lung Docs, our pulmonology specialists provide comprehensive evaluation, advanced diagnostics, and individualized treatment plans to identify the cause of pleural effusions and restore comfortable breathing.
Understanding Pleural Effusions
Pleural effusions can develop for many reasons, including infection, heart conditions, cancer, or inflammation. Some effusions are mild and resolve with treatment of the underlying cause, while others require more advanced intervention. Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the type of effusion and the most effective course of care.
Types of Pleural Effusions
Parapneumonic Pleural Effusions
Parapneumonic effusions develop as a complication of pneumonia or lung infections. They may range from simple fluid accumulation to more complex infections requiring drainage. Prompt diagnosis and treatment help prevent complications and support full recovery.
Malignant Pleural Effusions
Malignant pleural effusions occur when cancer cells affect the pleural space, often associated with lung cancer or cancers that have spread to the chest. These effusions may recur and cause ongoing shortness of breath. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, improving quality of life, and managing fluid buildup through targeted procedures and ongoing monitoring.
Heart Failure–Related Pleural Effusions
Heart failure can lead to fluid buildup throughout the body, including the pleural space. These effusions are often managed by treating the underlying heart condition while closely monitoring lung function and breathing symptoms.
Common Questions About Pleural Effusions
-
Common symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain (especially with deep breathing), cough, and fatigue. Some small effusions may cause no symptoms and are discovered on imaging.
-
Diagnosis typically includes chest X-rays, CT scans, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes fluid sampling (thoracentesis) to identify the cause of the effusion.
-
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the effusion. Options may include monitoring, medications, draining excess fluid, or treating the underlying condition such as infection, heart failure, or cancer.
-
Pulmonary nodules are typically found during imaging studies, such as:
Chest X-rays
CT scans
If a nodule is identified, additional testing may include:
Low-dose or high-resolution CT scans
PET scans
Pulmonary function tests
Biopsy procedures, when appropriate
These tests help determine the size, appearance, and behavior of the nodule.
-
Not always. Small or asymptomatic effusions may only require observation, while larger or symptomatic effusions may need drainage to improve breathing.
-
Yes, some pleural effusions—especially malignant or chronic effusions—can recur. Your pulmonologist will create a long-term management plan to reduce recurrence and control symptoms.
-
You should seek pulmonary care if you have unexplained shortness of breath, chest pain, or imaging that shows fluid around the lungs. Find a Lung Docs location near you to schedule an appointment.
Find a Location Near You
The Lung Docs provides specialized, state-of-the-art pulmonary care to our patients with asthma in Chattanooga and the surrounding Southeast Tennessee and Northwest Georgia areas.
PULMONOLOGIST
Dr. Mike Czarnecki
I’m Dr. Mike Czarnecki, “The Lung Doc,” and I’m trained in all areas of pulmonary health, including the diagnosis and treatment of asthma. I will work with you to formulate a personalized asthma treatment plan so you can live, laugh, love, and breathe better again! To book an appointment with me, call 423‑710‑3864 or request an appointment online. I can’t wait to meet you!